
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFC), Government of India, has issued a notification on rules for battery waste management in view of the shift to electric vehicles. Anticipating a need to have an organised channel for the safe disposal and recycling of batteries, the rules, called the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, are applicable to the producer, dealer, consumer, entities involved in collection, segregation, transportation, refurbishment and recycling of waste batteries.
All types of batteries, regardless of their chemistry, shape, volume, weight, material composition and use are covered under the rules. The rules also have a provision for penal action in case of a violation and imposition of environmental compensation. The ministry has also set a minimum recovery percentage target for recovered materials out of dry weight batteries.
The recovered materials will be then used to produce new batteries. For FY2024-25, the recovery target is set at 70 percent whereas for FY2025-26, it is 80 percent. The target for FY2026-27 is 90 percent. Mentioning that the recovery target may be reviewed by the committee once every four years to revisit the minimum levels of recovered battery materials in light of technical and scientific progress and emerging new technologies in waste management, the notification is expected to contribute towards enhancing each and every EV’s cost to the environment in India. This is especially in connection with the fact that nearly 1.4 million EVs as of July 2022 are said to operate in India if the data shared by the ministry of road transport and highways is relied upon. More than half of this volume is claimed to consist of electric three-wheelers followed by two-wheelers and passenger cars.
The PLI scheme and other policy changes in terms of manufacture and sale of electric vehicles, it is clear that a strong battery ELV and disposal policy has to be in place. From the cost to the environment point of view, a policy extension in terms of the manufacture of such batteries locally down to the fuel cell level should also taking into view the ability of the battery to perform efficiently through out its lifecycle, thus staying alive for longer and when it does die, it should be recyclable to a great extent.
Dr Akshay Singhal, Founder and CEO of Log9 Materials, averred. “The newly introduced Battery Waste Management standards by the Government under the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) concept addresses two important concerns. An efficient and effective waste management of all Li-Ion batteries that are nearing the end of their useful life and are expected to end up in landfills in a few years, avoiding any residual pollution impact. Second is the emphasis on investing in and nurturing the recycling of such used batteries, reducing the reliance on fresh resource mining.”

Shubham Vishvakarma, CEO and Chief of Process Engineering of Metastable Materials, said, “The Battery Waste Management Rules announced by the Government of India is an excellent and much-needed step towards bringing to the fore innovations and myriad growth opportunities for the battery waste management and battery treatment space in our country, especially at a time when the ongoing EV boom in India is leading us to increasing concerns on e-waste.” “Under the new Rules notified, the Government has mandated a minimum percentage of recovery of various materials from end-of-life batteries, which is bound to enable the growth of novel business models such as urban mining in order to reduce India’s foreign dependency on procuring raw materials for EV batteries and other types of batteries,” he added.

Ashok Sudrik, Chief Scientist, Infinite Orbit Research and Development Pvt Ltd, commented, “The Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, were much needed and we are happy that government has started taking cognizance of the hazardous waste being created and the recycling or waste collection. Other than waste management recycling rules, there is a need for manufacturers to incorporate extension of battery life technologies, keep the lithium content minimal and develop innovative cell chemistry. The life of a battery should be 4000 to 6000 cycles, which means a life spane of about 10 to 15 years. BaaS (Battery as a Service) concept with swappable batteries will be a big contributor to the ultimate goal of keeping cost to the environment low.”
In other parts of the world
In Canada, Li-Cycle will begin constructing a USD 175 million plant in Rochester, N.Y., for recycling of lithium-ion batteries. On the grounds of what used to be the Eastman Kodak complex, the plant will be the largest of its kind in North America with an eventual capacity of 25 metric kilotons of input material and a capability to recover 95 percent or more of cobalt, nickel, lithium and other valuable elements through zero-wastewater, zero-emissions process. Ajay Kochhar, Co-founder and CEO, Li-Cycle, said, “We'll be one of the largest domestic sources of nickel and lithium, as well as the only source of cobalt in the United States."
In May 2022, Hydrovolt, the largest battery recycling plant in Europe started operations in Fredrikstad, Norway. A joint venture between two Norwegian companies – Hydro and Northvolt, the plant has the capacity to process 12,000 tonnes of battery packs per year, enough for the entire end-of-life battery market in Norway currently. Claimed to have the capability to recover 95 percent of the materials used in an EV battery including plastics, copper, aluminum and ‘black mass’, a powder containing various elements inside lithium-ion batteries like nickel, manganese, cobalt and lithium.
Not just in Europe or US, the rise of Electric Vehicles (EVs) and associated battery gigafactories is pushing forward the creation of a battery recycling value chain. It is a matter of debate whether it got to be a close-loop or an open-loop design in terms of sourcing of batteries to recycle and to put the resulting material to good use so that the cost to the environment is kept minimal. As the demand for use of ‘green’ electricity source gathers pace the world over, on the other end of the spectrum, which involved the end-of-life vehicle for EVs, the demand for recycling in increasing partly due to regulations – the EU regulations have just intensified – and partly by a demand for re-use of materials due to geo-political reasons as well. A strong desire to localise supply chains and safeguard critical raw materials are also the driving factors.
Marelli's Zone Control Unit Named Engineering Product of the Year
- By MT Bureau
- March 13, 2026
Tier 1 automotive supplier Marelli has received the ‘Commendable’ honour in the ‘Engineering Product of the Year’ category at the Digital Engineering Awards 2026. The ceremony, hosted by L&T Technology Services in association with ISG and CNBC-TV18, was held in Boston, USA, on 12 March 2026.
The award recognises the role of Marelli’s Zone Control Unit (ZCU) in the transition towards software-defined vehicles.
The ZCU is designed to replace traditional domain-based architectures with a platform that delivers cross-domain control through a single Electronic Control Unit (ECU). This system simplifies vehicle electrical and electronic (E/E) layouts and enables communication across vehicle zones. By reducing the number of dedicated ECUs and streamlining wiring, the ZCU reduces wiring harness weight by 30 per cent compared to existing systems.
It is built on the EliteZone platform and supports ethernet capabilities, hardware accelerators, and remote-control protocols. It features processing performance up to 6 KDMIPS, two-port Gigabit Ethernet, and more than 20 CAN and LIN interfaces. The unit also includes an integrated hypervisor and data routing engine, supporting functional safety up to ASIL D standards.
For power management, the ZCU accommodates 48V system requirements with dedicated power input and efuse-protected output. The hardware uses a service-oriented architecture (SOA), which decouples software development from hardware. This approach allows modules to subscribe to services exposed by the ECU, supporting feature updates throughout the vehicle lifecycle and shortening development cycles for manufacturers.
Ravi Tallapragada, President, Marelli’s Electronics business, stated, “This recognition for our Zone Control Unit makes me and all of us at Marelli truly proud. It reflects the impact of our work on supporting the industry’s transition toward software-defined vehicles. By bringing cross-domain control into a single, scalable platform, our ZCU enables vehicle makers to innovate at speed. I want to congratulate our global engineering teams, whose dedication and expertise made this achievement possible.”
drivebuddyAI Receives Patent For Vehicle Facial Recognition System
- By MT Bureau
- March 12, 2026

drivebuddyAI has been awarded a patent for a facial recognition system designed for vehicle environments. The technology identifies drivers in moving vehicles to monitor duty hours and manage fatigue.
The system uses computer vision and artificial intelligence to recognise faces under varying lighting conditions and when drivers wear accessories such as caps or mufflers. This replaces manual or key-based identification methods to track driving time for wage calculations and safety compliance.
The patented technology is integrated into several areas of the company's product suite:
- Driver Profiling: Used in the 'CARDs' scoring method.
- Alert Systems: Provision of language-specific alerts based on driver identification.
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time tracking of duty time and driver behaviour.
- Compliance: Alignment with Indian government discussions on enforcing rest periods for commercial vehicle operators.
The company holds 15 patents in AI vision, edge processing, and risk assessment. Its systems meet India's AIS-184 driver monitoring standards and the European Union's General Safety Regulation (GSR) 2144.
Nisarg Pandya, CEO, drivebuddyAI, said, “Driver fatigue remains one of the most critical yet under-addressed causes of highway accidents. Our patented technology ensures that fleets know exactly who is driving, for how long, and under what conditions. This creates a foundation for enforcing safe driving limits while also enabling continuous learning and improvement for drivers. This milestone reflects our commitment to delivering technology built from the ground up and leveraging AI to enable safer and smarter driving solutions.”
Servotech And Electra EV Secure Joint Patent For Low-Voltage EV Charging
- By MT Bureau
- March 11, 2026

Servotech Renewable Power System and Electra EV have been granted a patent by the Indian Patent Office for an ‘Electric Vehicle Charging Device’. The technology is designed to provide charging solutions for low-voltage electric vehicles (EVs).
The device addresses interoperability challenges by enabling fast DC charging for low-voltage EVs with sub-200V DC platforms. This includes vehicles based on GB/T Bharat DC 001 standards. The technology allows these vehicles to utilise widely deployed, conventional high-voltage CCS2 charging infrastructure.
The patented device incorporates power management and voltage conversion systems to facilitate energy transfer to low-voltage battery platforms. The primary focus of the technology is on vehicle segments such as small commercial EVs and pick-up vans, which are used for urban and last-mile mobility.
Key features of the technology include:
- Interoperability: Enables sub-200V DC platforms to use CCS2 fast-charging stations.
- Compatibility: Supports vehicles adhering to GB/T Bharat DC 001 standards.
- Energy Management: Advanced voltage conversion to ensure safe battery charging.
- Safety: Integrated protocols for stable energy transfer.
The joint ownership of the patent by Servotech and Electra EV is intended to accelerate the development of charging infrastructure for small commercial fleets. The demand for such flexible solutions has increased as adoption of low-voltage EVs grows within the Indian logistics and transport sectors.
Arun Handa, CTO, Servotech Renewable Power System, said, “Securing this patent is an important step in strengthening our innovation-led approach to EV charging technology. Low-voltage electric vehicles are a key part of India’s mobility ecosystem, particularly in segments like small commercial fleets. This patented device has been designed to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable charging for such vehicles, helping make EV adoption through improved charging compatibility.”
- NXP Semiconductors
- Z248
- NXP CoreRide Z248
- 48V
- Sebastien Clamagirand
- Peter Gliwa
- GLIWA
- Jochen Rein
- Vector
NXP Introduces CoreRide Z248 Zonal Reference System For 48V Architectures
- By MT Bureau
- March 11, 2026
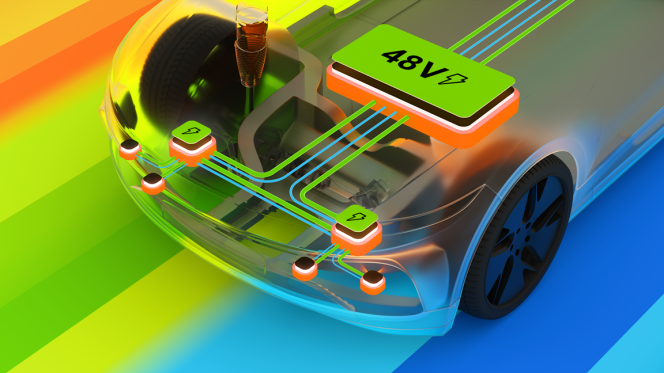
NXP Semiconductors has launched the NXP CoreRide Z248, a zonal reference system combining 48V energy distribution with data routing. The hardware-software foundation is designed to assist OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers in transitioning to software-defined vehicle (SDV) architectures by reducing integration effort and development cycles.
The Z248 is built on NXP’s S32K5 microcontroller series, featuring on-chip Magnetic Random Access Memory (MRAM). This technology is intended to accelerate electronic control unit (ECU) programming during manufacturing and over-the-air (OTA) updates.
The system integrates several 48V-capable components and networking tools:
- Power Management: Includes eFuses, Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMICs), and DC-DC converters for energy conversion and protection.
- Networking: Features Ethernet PHY and CAN transceivers for data handling.
- Software Stack: A pre-validated stack managing smart data energy network (SDEN) functions such as impedance monitoring and diagnostics.
- Safety: Built-in functional safety and real-time responsiveness for zonal processing.
NXP stated it has validated the Z248 through system-level tests focusing on low-power modes and wake-up response times. The package includes a Board Support Package (BSP) with integrated software from partners including GLIWA for performance monitoring, Green Hills Software for compilers and Vector for embedded tools.
The reference system is designed for deployment across internal combustion engine (ICE), hybrid, and battery electric vehicle (BEV) platforms. It supports ECU consolidation by managing energy distribution and data protocols within a single architecture.
Sebastien Clamagirand, SVP and General Manager, Automotive Systems & Platforms, NXP Semiconductors, said, “The NXP CoreRide zonal reference system Z248 delivers a performance-optimized, scalable 48 V foundation that intelligently fuses power, data and software, while dramatically simplifying system integration, reducing time to market, and enabling OEMs to focus on vehicle differentiation and long‑term value creation.”
Peter Gliwa, CEO and Founder, GLIWA, added, “NXP understood that the eco-system, the tooling around a new platform is essential for its success. With our Analysis Suite T1 built into the NXP CoreRide Z248 zonal reference system, high efficiency, proper timing analysis and timing verification are very well addressed.”
Jochen Rein, SVP Business Unit Software Platform, Vector, stated, “The combination of the NXP CoreRide platform and Vector’s software foundation provides a robust basis for next‑generation zonal architectures. We enable our joint customers to reduce their time- to-market due to a pre-integrated and highly optimized software stack.”






Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT