Robust, Smart Charging Network Needed To Boost EV Proliferation
- By 0
- April 05, 2020

.jpg)
Q: India is the first country outside of Europe where you are operating. Why this entry?
Jha: The Indian market is different from the Nordic and European markets, and it is the first country outside Europe, where Fortum entered the electric vehicle charging space in 2017. We have integrated a couple of Indian chargers into our system and this enables us to deploy ‘Made in India’ chargers to our network. This will give our customers the freedom to choose the chargers, their availability, price and other benefits.
Fortum established its first charging station in New Delhi in 2017. Its services in India include owning charging infrastructure, operating other’s charging infrastructure network using Fortum’s own cloud-based charging system and selling Fortum’s proven off-the-shelf cloud system to other operators to manage charging infrastructure in the B2B segment.
Q: How do you see and predict the EV market in India?
Jha: India will benefit from the global growth of EV technologies and can reach a maturity stage faster than in other countries. As Tesla did for the US market, start-ups in India are poised to promote the adoption of EVs. Free from any legacy baggage, they are able to offer pure electric vehicles as is evident on the road, particularly in the two and three-wheeler sector. Traditional OEMs also are trying to hold on to their market share. Hyundai has taken the lead by introducing Kona. The electric version of Maruti cars can be seen on the road though in test mode. More than ten models of electric vehicles are slated for launch in the next 12-18 months. Tata Motors has announced plans to introduce more models of the electric variant. Mahindra promises to launch KUV 100 and SUV 300 with the electric powertrain. With India poised to become the third-largest auto market in the world, none of the players would like to miss this great opportunity.
With more and more renewable energy being fed into the grid, the use of EVs will provide the flexible load to balance the system.
Q: What are the fundamental differences between India and Europe in terms of vehicle requirements and charging infrastructure?
Jha: India and Europe share a common requirement in the automobile space. India generally follows the European automotive emission norms as Euro 6. Europe started the EV journey with high voltage system cars like Nissan Leaf, which warrants a different set of chargers to offer good customer experience. Starting from 50kW DC chargers, Europe has moved to high power charging capacity of 350kW in DC mode which brings down the charging time to about 10 minutes for a 150-200km range. On the AC side in public charging, it has a network of 22kW chargers which offer semi-fast charging to most of the vehicles. The 3.3 kW AC chargers are generally deployed at home and parking places.
India, on the other hand, has a different vehicle composition. Most of its EVs are two and three-wheelers which have a different kind of charging need. They are currently dominated by lead-acid batteries. In the four-wheeler passenger car segment also, India started with a unique product. The available cars are on low voltage battery system, which requires a different set of chargers – 15/20 kW power in DC mode. They need longer charging time than their counterparts in Europe where a car with almost double the size of battery can get charged in nearly half the charging time than in India. Now, a few OEMs have started selling high voltage system cars which would require 50kW charging infrastructure.
Another significant difference between Europe and India is the need for public charging. Most of the European countries have single-family low-rise homes with garage whereas Indian cities like Delhi have mostly unorganised street parking. This fundamentally alters the need of charging infrastructure in India. While in Europe home charging would be dominating, India will need public charging as the dominant mode.
.jpg) Q: Charging infrastructure and time is probably the biggest hindrance in the adaptation of EVs in India? How do you find opportunities in this area?
Q: Charging infrastructure and time is probably the biggest hindrance in the adaptation of EVs in India? How do you find opportunities in this area?
Jha: Three major interdependent stakeholders influence the evolvement of EVs in any country. They are: automobile manufacturers, battery manufacturers, and charging infrastructure providers. Given the limited use of e-vehicles in India now, the infrastructure for the same is also at a very nascent stage. The lack of sufficient infrastructure could be the most common reason for the range concern that directly affects the consumer behaviour and potential of EV sales in India. However, from the operators’ point of view, it is difficult to invest in charging infrastructure without an existing demand for charging services.
India will need ubiquitous public charging networks. India needs millions of charging points once all cars sales happen on the electric platform. This offers huge opportunity for both the private and the public sectors. However, considering the space constraint and inadequate electricity infrastructure, setting up such a massive network of public charging will be a demanding task. Government support will be required in making locations available for this purpose if we have to roll out a good network of charging stations.
For EVs to be acceptable, consumers have to be assured of the availability of charging stations like fuel stations for ICE vehicles. A robust charging station network would give them confidence, and that would work as a pull effect on OEMs.
Q: India is a vast country. How are you going to identify and target the regions or pockets where EV adaptation will be faster?
Jha: As it happens with any new technological product, initially EV will be adopted by innovators or early adopters. We expect that these vehicles will be adopted mostly in cities with the highest per capita income. We operate now in five cities: Delhi-NCR, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad and Ahmedabad. We have 66 DC public charging points. Since the launch of our DC fast-charging stations in Hyderabad, we have seen positive adoption of electric vehicles by customers. We have more than 900 registered users, and more than 1500 customers have downloaded our mobile app. These are smart chargers which are unmanned and give freedom to the consumer to charge their vehicles at the location of their choice, and at their convenience.
Q: Do you think public utility places would play a more prominent role in increasing the number of EV charging stations? Could you highlight Fortum India’s partnership with Indian Oil?
Jha: We provide our bit in creating reliable and smart charging infrastructure. Our first DC fast public charging station in Hyderabad came up at IOC COCO retail outlet at Begumpet. We are operating 16 charging points at eight retail outlets of IOC in Hyderabad. We demonstrated our capability of operating smart chargers by unveiling the charging of Mahindra e2oplus remotely from Hotel ITC Kakatiya, Hyderabad, using Fortum Charge & Drive Mobile App.
Q: How many EV charging stations has Fortum India set up so far, and what is the immediate target?
Jha: Fortum has made 66 DC Fast charging points operational in Delhi-NCR, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Ahmedabad. Fortum Charge & Drive also offers a cloud solution to EV charging service providers and infrastructure investors.
Recently, we have established India’s first public charging network of 50 kW DC chargers at dealership locations of MG Motors. Any car owner can access these stations if the car is compatible with CCS/CHAdeMO standards. We are continuously evaluating opportunities across the country.
Q: How do you see the role of the stakeholders such as charging station infrastructure manufacturers, energy companies and operators in the growth of EV adoption?
Jha: Each stakeholder has a role to play in EV adoption in India. It is important to note that it is the vehicle and its battery system which determines the charging infrastructure need, not otherwise. The charging standards or capacity of chargers or time of charging, and everything is dependent on the design of the battery and its management system adopted by the OEMs. Charging manufacturers and operators follow the demand. In charging ecosystem, manufacturer caters to the supply side by offering his product which can be put to use by charge point operators at strategic locations. Energy distribution companies also have a critical role to play. EV charging, particularly public charging in DC mode, requires high capacity which might need augmentation of electricity infrastructure. Energy to Charge Point Operators (CPOs) should be provided at a reasonable price so that end-consumers can charge their vehicles at affordable prices. Efforts of all these stakeholders have to get aligned.
Q: What have been the ground-level challenges for Fortum India?
Jha: Access to a suitable location and electricity supply is a major challenge. The number of EVs initially will be less, so also the business for the Charge Point Operators. It will be more challenging if CPOs have to pay rent for the space or bear any upfront cost on electricity infrastructure. So it is expected that these two parts would be taken care of by the government or partners to make EVs affordable for the customers.
Q: Being in the EV charging station space, what do you expect from the government?
Jha: For the manufacture of EVs and the growth of the industry, the government introduced the FAME scheme. It would also support the manufacturing of advanced batteries which will accelerate the adoption of EVs by bringing down the cost of the battery. Tax reduction is a significant boost for the consumer as it would push the EV price to inch towards ICE vehicle price.
Creating a robust and smart charging network should be the focus. Although through FAME-II the government has called for proposals on the setting up of 1000 electric vehicle charging stations in the country, this is not enough. Consumers would like to have charging points at their preferred locations, time, and price to avoid range anxiety. This requires a robust, ubiquitous, and friendly charging network of stations. As charging takes more time than gasoline refuelling, the consumer would like to find a charging station in an exciting place where he would feel happy to spend time while the vehicle gets charged.
We have to add lakhs of charging points year after year if in future all vehicles sold are electric. This would require access to space, which is scarce, particularly in urban areas. Augmented electricity infrastructure would be needed at the local network level even though at the national level this will not be significant. So if the government finds some ways to offer space and upgrades electricity connections on the plug-and-play mode to CPOs it will give a boost to the creation of charging infrastructure.
EV charging would be a different proposition. Unlike oil and CNG, this has interdependency of battery and electricity. Appropriate communication is needed between battery and charger, and charge and grid, to ensure safety and reliability to the vehicle and grid. This necessitates that charging infrastructure must be smart. This would also warrant a smart grid. What is needed is a greater and urgent push towards upgradation and strengthening of both electricity and charging infrastructure. (MT)
Marelli's Zone Control Unit Named Engineering Product of the Year
- By MT Bureau
- March 13, 2026
Tier 1 automotive supplier Marelli has received the ‘Commendable’ honour in the ‘Engineering Product of the Year’ category at the Digital Engineering Awards 2026. The ceremony, hosted by L&T Technology Services in association with ISG and CNBC-TV18, was held in Boston, USA, on 12 March 2026.
The award recognises the role of Marelli’s Zone Control Unit (ZCU) in the transition towards software-defined vehicles.
The ZCU is designed to replace traditional domain-based architectures with a platform that delivers cross-domain control through a single Electronic Control Unit (ECU). This system simplifies vehicle electrical and electronic (E/E) layouts and enables communication across vehicle zones. By reducing the number of dedicated ECUs and streamlining wiring, the ZCU reduces wiring harness weight by 30 per cent compared to existing systems.
It is built on the EliteZone platform and supports ethernet capabilities, hardware accelerators, and remote-control protocols. It features processing performance up to 6 KDMIPS, two-port Gigabit Ethernet, and more than 20 CAN and LIN interfaces. The unit also includes an integrated hypervisor and data routing engine, supporting functional safety up to ASIL D standards.
For power management, the ZCU accommodates 48V system requirements with dedicated power input and efuse-protected output. The hardware uses a service-oriented architecture (SOA), which decouples software development from hardware. This approach allows modules to subscribe to services exposed by the ECU, supporting feature updates throughout the vehicle lifecycle and shortening development cycles for manufacturers.
Ravi Tallapragada, President, Marelli’s Electronics business, stated, “This recognition for our Zone Control Unit makes me and all of us at Marelli truly proud. It reflects the impact of our work on supporting the industry’s transition toward software-defined vehicles. By bringing cross-domain control into a single, scalable platform, our ZCU enables vehicle makers to innovate at speed. I want to congratulate our global engineering teams, whose dedication and expertise made this achievement possible.”
drivebuddyAI Receives Patent For Vehicle Facial Recognition System
- By MT Bureau
- March 12, 2026

drivebuddyAI has been awarded a patent for a facial recognition system designed for vehicle environments. The technology identifies drivers in moving vehicles to monitor duty hours and manage fatigue.
The system uses computer vision and artificial intelligence to recognise faces under varying lighting conditions and when drivers wear accessories such as caps or mufflers. This replaces manual or key-based identification methods to track driving time for wage calculations and safety compliance.
The patented technology is integrated into several areas of the company's product suite:
- Driver Profiling: Used in the 'CARDs' scoring method.
- Alert Systems: Provision of language-specific alerts based on driver identification.
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time tracking of duty time and driver behaviour.
- Compliance: Alignment with Indian government discussions on enforcing rest periods for commercial vehicle operators.
The company holds 15 patents in AI vision, edge processing, and risk assessment. Its systems meet India's AIS-184 driver monitoring standards and the European Union's General Safety Regulation (GSR) 2144.
Nisarg Pandya, CEO, drivebuddyAI, said, “Driver fatigue remains one of the most critical yet under-addressed causes of highway accidents. Our patented technology ensures that fleets know exactly who is driving, for how long, and under what conditions. This creates a foundation for enforcing safe driving limits while also enabling continuous learning and improvement for drivers. This milestone reflects our commitment to delivering technology built from the ground up and leveraging AI to enable safer and smarter driving solutions.”
Servotech And Electra EV Secure Joint Patent For Low-Voltage EV Charging
- By MT Bureau
- March 11, 2026

Servotech Renewable Power System and Electra EV have been granted a patent by the Indian Patent Office for an ‘Electric Vehicle Charging Device’. The technology is designed to provide charging solutions for low-voltage electric vehicles (EVs).
The device addresses interoperability challenges by enabling fast DC charging for low-voltage EVs with sub-200V DC platforms. This includes vehicles based on GB/T Bharat DC 001 standards. The technology allows these vehicles to utilise widely deployed, conventional high-voltage CCS2 charging infrastructure.
The patented device incorporates power management and voltage conversion systems to facilitate energy transfer to low-voltage battery platforms. The primary focus of the technology is on vehicle segments such as small commercial EVs and pick-up vans, which are used for urban and last-mile mobility.
Key features of the technology include:
- Interoperability: Enables sub-200V DC platforms to use CCS2 fast-charging stations.
- Compatibility: Supports vehicles adhering to GB/T Bharat DC 001 standards.
- Energy Management: Advanced voltage conversion to ensure safe battery charging.
- Safety: Integrated protocols for stable energy transfer.
The joint ownership of the patent by Servotech and Electra EV is intended to accelerate the development of charging infrastructure for small commercial fleets. The demand for such flexible solutions has increased as adoption of low-voltage EVs grows within the Indian logistics and transport sectors.
Arun Handa, CTO, Servotech Renewable Power System, said, “Securing this patent is an important step in strengthening our innovation-led approach to EV charging technology. Low-voltage electric vehicles are a key part of India’s mobility ecosystem, particularly in segments like small commercial fleets. This patented device has been designed to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable charging for such vehicles, helping make EV adoption through improved charging compatibility.”
- NXP Semiconductors
- Z248
- NXP CoreRide Z248
- 48V
- Sebastien Clamagirand
- Peter Gliwa
- GLIWA
- Jochen Rein
- Vector
NXP Introduces CoreRide Z248 Zonal Reference System For 48V Architectures
- By MT Bureau
- March 11, 2026
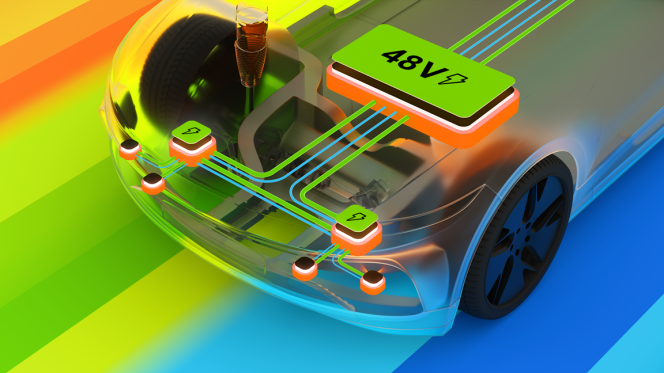
NXP Semiconductors has launched the NXP CoreRide Z248, a zonal reference system combining 48V energy distribution with data routing. The hardware-software foundation is designed to assist OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers in transitioning to software-defined vehicle (SDV) architectures by reducing integration effort and development cycles.
The Z248 is built on NXP’s S32K5 microcontroller series, featuring on-chip Magnetic Random Access Memory (MRAM). This technology is intended to accelerate electronic control unit (ECU) programming during manufacturing and over-the-air (OTA) updates.
The system integrates several 48V-capable components and networking tools:
- Power Management: Includes eFuses, Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMICs), and DC-DC converters for energy conversion and protection.
- Networking: Features Ethernet PHY and CAN transceivers for data handling.
- Software Stack: A pre-validated stack managing smart data energy network (SDEN) functions such as impedance monitoring and diagnostics.
- Safety: Built-in functional safety and real-time responsiveness for zonal processing.
NXP stated it has validated the Z248 through system-level tests focusing on low-power modes and wake-up response times. The package includes a Board Support Package (BSP) with integrated software from partners including GLIWA for performance monitoring, Green Hills Software for compilers and Vector for embedded tools.
The reference system is designed for deployment across internal combustion engine (ICE), hybrid, and battery electric vehicle (BEV) platforms. It supports ECU consolidation by managing energy distribution and data protocols within a single architecture.
Sebastien Clamagirand, SVP and General Manager, Automotive Systems & Platforms, NXP Semiconductors, said, “The NXP CoreRide zonal reference system Z248 delivers a performance-optimized, scalable 48 V foundation that intelligently fuses power, data and software, while dramatically simplifying system integration, reducing time to market, and enabling OEMs to focus on vehicle differentiation and long‑term value creation.”
Peter Gliwa, CEO and Founder, GLIWA, added, “NXP understood that the eco-system, the tooling around a new platform is essential for its success. With our Analysis Suite T1 built into the NXP CoreRide Z248 zonal reference system, high efficiency, proper timing analysis and timing verification are very well addressed.”
Jochen Rein, SVP Business Unit Software Platform, Vector, stated, “The combination of the NXP CoreRide platform and Vector’s software foundation provides a robust basis for next‑generation zonal architectures. We enable our joint customers to reduce their time- to-market due to a pre-integrated and highly optimized software stack.”






Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT